pleural effusion cat lymphoma
However they do not contain chylomicrons and therefore do not. Pleural effusion can have a number of different causes including diseases of the heart lungs or other systemic diseases.
Cats of the Siamese breed are overrepresented.

. Tumors in the lungs or chest wall can lead to pleural effusion. EATCL type II is associated with indolent clinical behavior and prolonged. Six cats 375 were positive for feline leukaemia virus and three cats 187 were positive for feline immuno-deficiency virus.
The volume of the effusion may be scant and mainly of diagnostic significance or so large as to. Objectives Non-chylous lymphorrhagic pleural effusions are transudative effusions with a predominance of lymphocytes. Fluid overload in cats most commonly during fluid therapy Lung lobe torsion.
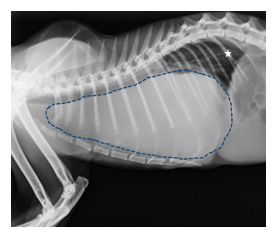
Other causes included pyothorax idiopathic chylothorax trauma FIP nontraumatic diaphragmatic hernia vasculopathy uremic pleuritis. Feline mediastinal lymphoma commonly occurs in young cats with a median age at diagnosis of three years and has commonly been associated with a positive FeLV status. Pleural effusion can be confirmed with radiography a single DV view if patient permits or thoracic.
Feline lymphoma is a malignant cancer of the lymphatic system the exquisitely structured arrangement of internal organs and tissues that directly or indirectly influences virtually every. Feline infectious peritonitis. Get NHVs Lymphoma Gold Support Pack Today.
Most cats with alimentary lymphoma are FeLV ELISA negative. Cats may develop open-mouthed breathing in. Ad Help keep your pet comfortable in their fight against lymphoma.
Exudate effusion is generally due to inflammation or. The most common causes for pleural effusion in all 380 cats were found to be CHF n155 408 and neoplasia n98 258. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma was the most.
Cats with pleural effusion often have rapid shallow breathing and pet owners may notice increased respiratory effort. Thoracic radiography is useful if clinical suspicion of respiratory disease but uncommon to see. Either way the prognosis is.
Pertinent findings included a high occurrence of pleural effusion with mediastinal lymphoma and other types of intrathoracic neoplasia pyothorax cardiomyopathy and feline infectious. This occurs in cats either because too little. Palpable mass facial deformity pleural effusion and positive FeLV status will raise the index of suspicion for large cell lymphoma.
This syndrome is caused by infection with a mutated form of a feline coronavirus. A cytology evaluation of the pleural fluid strongly suggested a lymphoma containing variable sized. Pleural effusion is the abnormal accumulation of fluid within the chest cavity which is lined by a membrane -- the pleural lining.
Form of feline lymphoma arises from diffuse mucosal associated lymphoid tissue MALT of the small. Cats presenting with pleural effusion are nearly always in respiratory distress ranging from an increased respiratory rate and effort to open mouth breathing. Classification of pleural effusion PE is central to diagnosis.
Trauma is an uncommonly recognized cause of chylothorax in dogs and cats because the thoracic duct. Pleural effusion is a pathologic accumulation of fluid within the pleural space. Rapid breathing Breathing with an open mouth Lethargy Lack of appetite Weight loss Chest pains Fever Coughing Unusual positions while sitting or lying down Blue tongue or gums.
Up to 25 cash back With pleural effusion youre usually dealing with one of two things- Lymphoma cancer or CHF congestive heart failure. Some of the symptoms of pleural effusion include the following. Pleural effusion or pericardial effusion can cause muffled heart sounds.
Chronic inflammation may be associated with development of lymphoma. Traditional veterinary classification has distinguished between transudates modified transudates and exudates. Thoracic radiography is useful if clinical suspicion of respiratory disease but uncommon to see.
The thoracic radiographs revealed significant pleural effusion. Chronic inflammation may be associated with development of lymphoma. Four standard effusion types recognized in addition to blood.
Chylothorax has been reported in a cat after ligation of the left brachycephalic vein. Mediastinal--most cats with mediastinal lymphoma are relatively young and FeLV ELISA positive. Accumulation of fluid in the pleural space.

Lymphoma In Cats Veterinary Partner Vin

Read About Oncology In This Article By Leanne N Twomey And Rick A Alleman

Feline Lymphoma Clinician S Brief
Feline Lymphoma Clinician S Brief
Feline Lymphoma Clinician S Brief
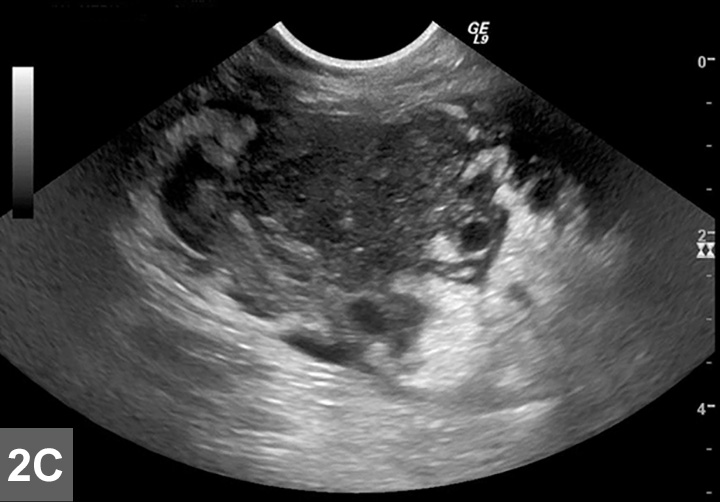
Case Report Mediastinal Lymphoma In Cat Alicia Moj Anatomy Physiology
Feline Lymphoma What Your Need To Know The Animal Medical Center

Lymph Node Ferret No 12 Anaplastic Large T Cell Lymphoma Download Scientific Diagram
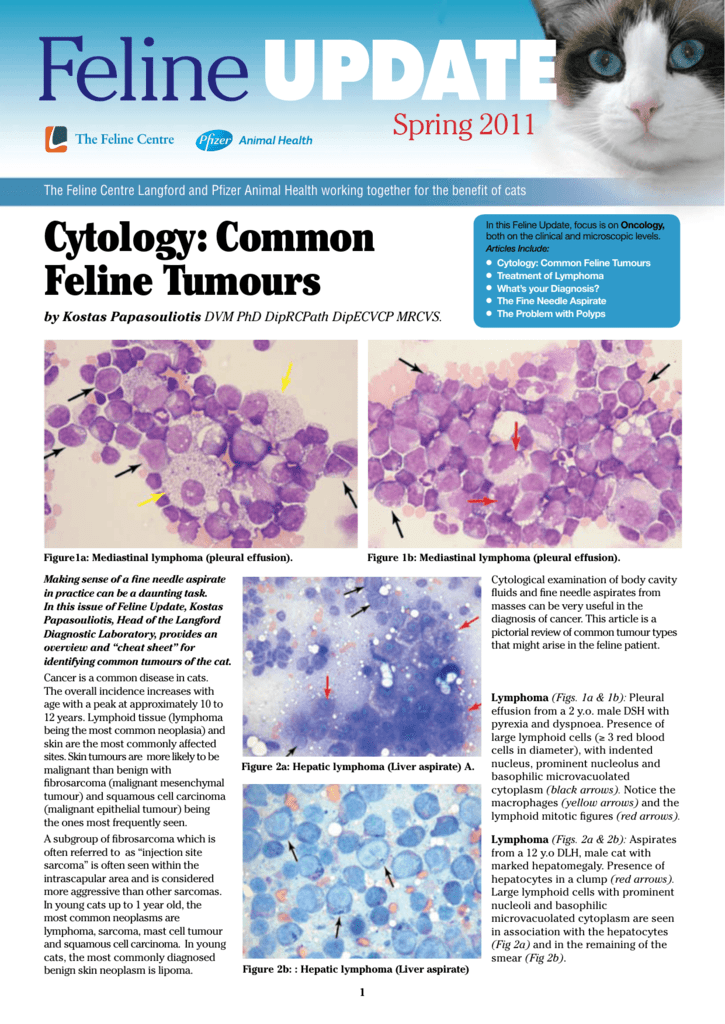
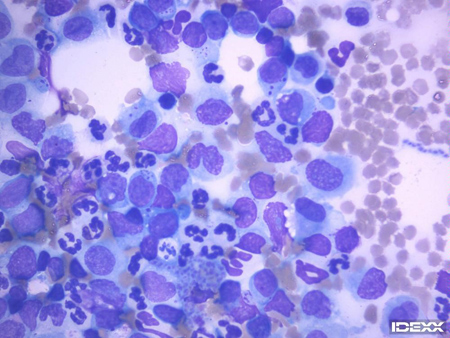
Cytology Common Feline Tumours

Feline Lymphoma Clinician S Brief

A Histology From Medium Size B Cell Pericardial Lymphoma Of Cat 2 Download Scientific Diagram
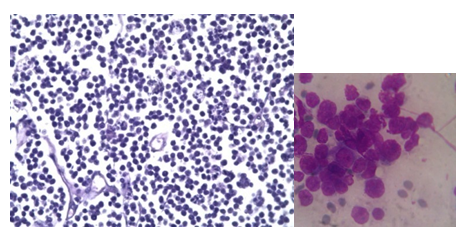
Case Report Mediastinal Lymphoma In Cat Alicia Moj Anatomy Physiology

Feline Lymphoma Clinician S Brief

Pin By Dr Abuaiad On Lymphatics Nuclear Medicine Spinal Lesion Spinal

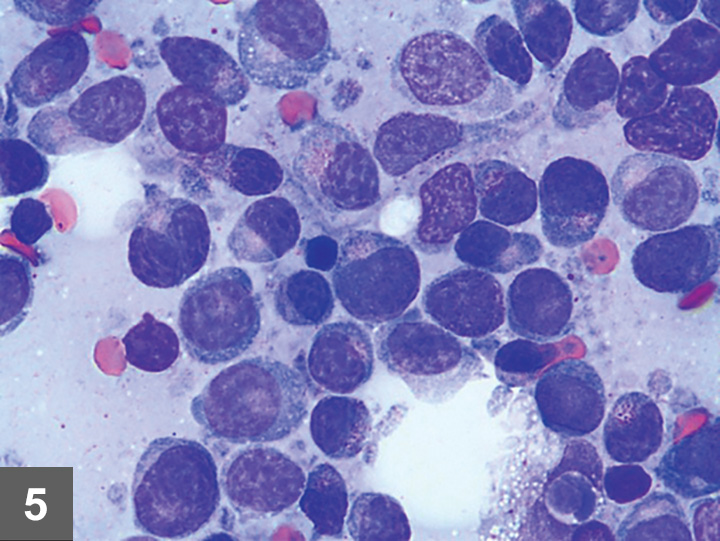
Pleural Effusion Fine Needle Aspirate Mediastinal B Cell Lymphoma Download Scientific Diagram
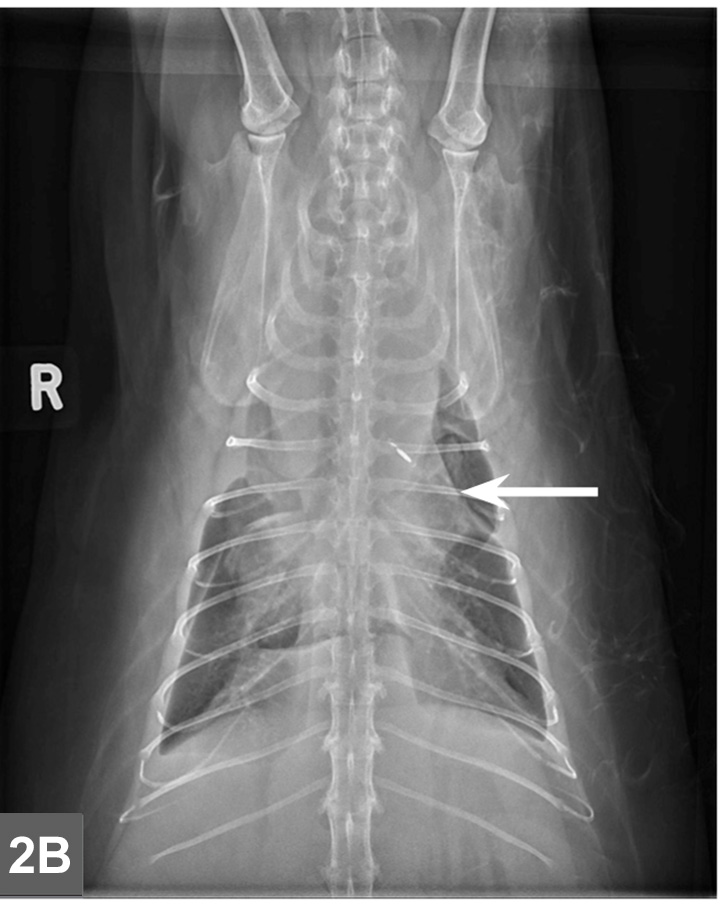
Feline Lymphoma Clinician S Brief

Figure 3 From Pericardial Lymphoma In Seven Cats Semantic Scholar

